Stainless Steel Demister Pads: Specs, Sizes, and Types
Stainless steel demister pads are essential in industries like gas cleaning, chemical processing, oil and gas, HVAC, and refineries. They efficiently remove liquid droplets from gas streams, improving performance and protecting equipment.
- Materials and Construction: These pads are built from corrosion-resistant stainless steel (typically 304 or 316) using woven wire (0.1-1.0 mm wire, 50-500 holes/inch), expanded metal (0.5-5 mm holes), or felted material.
- Size and Dimensions: Thickness varies from 0.5 to 5 mm. Woven wire types have wire diameters of 0.1-1.0 mm and 50-500 holes per inch. Expanded metal pads feature 0.5-5 mm hole sizes. Standard panel sizes range from 300×300 mm to 1000×1000 mm, with custom sizes and shapes available.
- Performance and Efficiency: Demister pads are rated based on their droplet capture ability (usually 1-10 µm). They cause minimal pressure drop (a few to tens of mmWC). Gas flow capacity is measured in m³/h or SCFM.
- Operating Conditions: They can operate in temperatures from below freezing up to 300–400 °C. Stainless steel offers resistance to many chemicals and can handle specific pressure requirements.
- Classification and Standards: These pads meet industry standards like API, ASME, and ISO. They are classified by efficiency: high-efficiency for fine droplets and standard for larger ones. Custom designs are also possible.
- Installation and Maintenance: Demister pads are installed in easily accessible header boxes or separators, often in single or multiple layers. Regular inspection and cleaning are needed, though some models are self-cleaning.
- Customization: Options include materials, coatings, and shapes. The use of stainless steel ensures durability and long-term cost-effectiveness.
Demister Pads with Classic Design
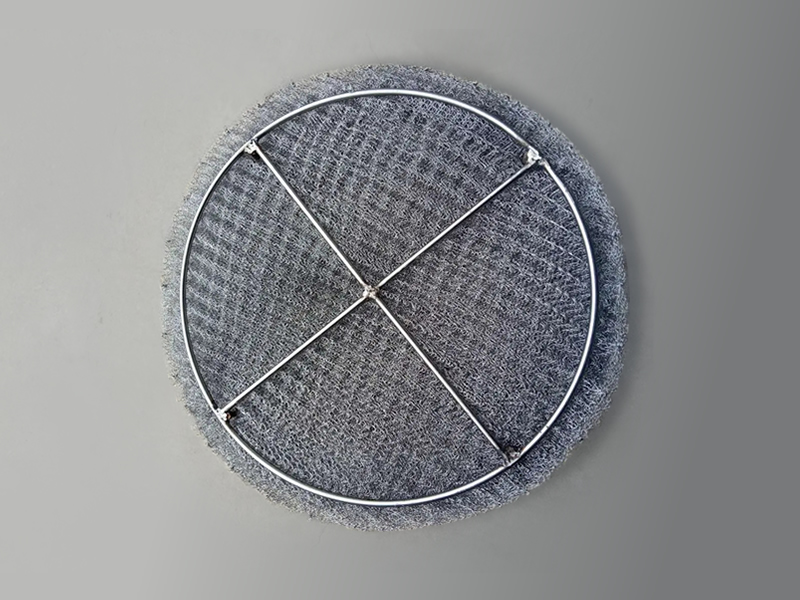

Diameter: Typically 800 mm, smaller for compact installations.
Thickness: 100 mm, suitable for moderate mist loads.
Construction: Single, unified structure with integrated bar grating.
Reinforcement: Bar grating enhances rigidity.
Application: Ideal for smaller vessels needing quick, easy installation.
Handling: Easier storage and transport as one unit.
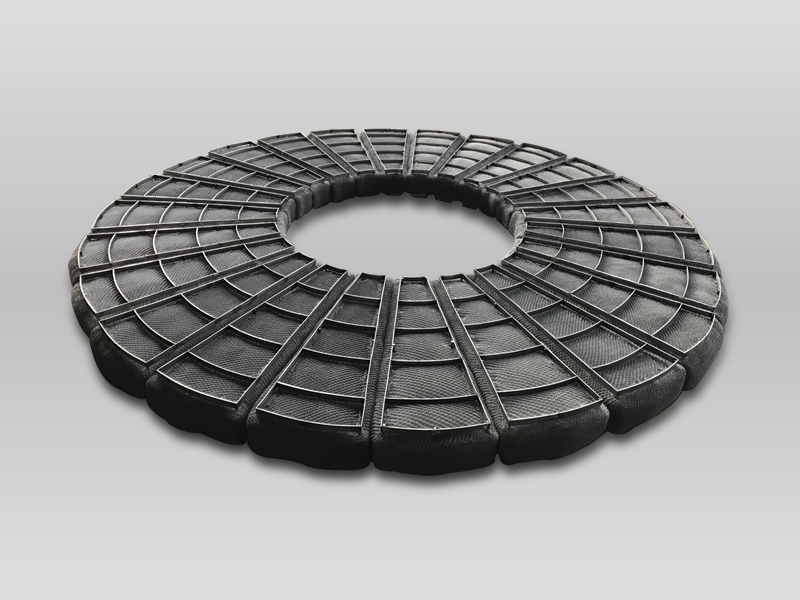

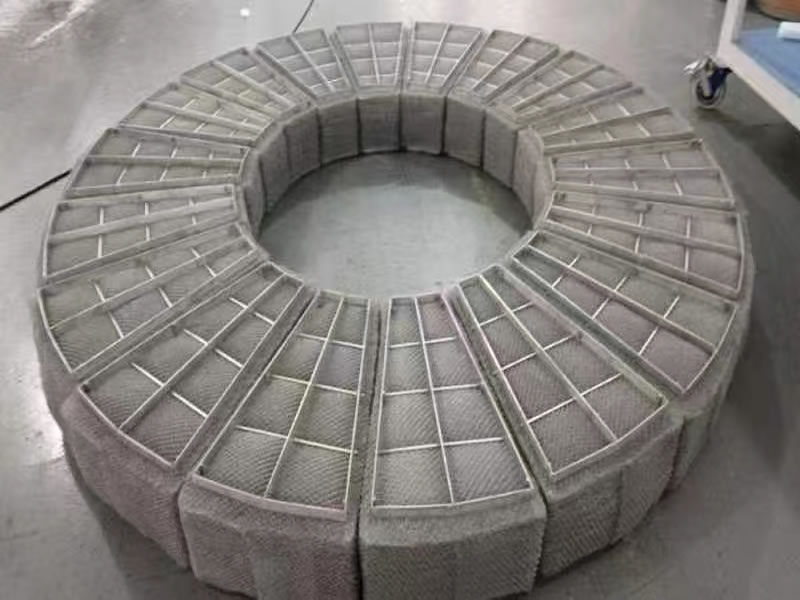
Diameter: Around 1,200 mm, significantly larger.
Thickness: 100–150 mm (variable by segment).
Construction: Multiple curved segments.
Reinforcement: Framing or bracing on segments.
Application: Best for large, confined vessels.
Handling: Segmented form eases transport in tight spaces.
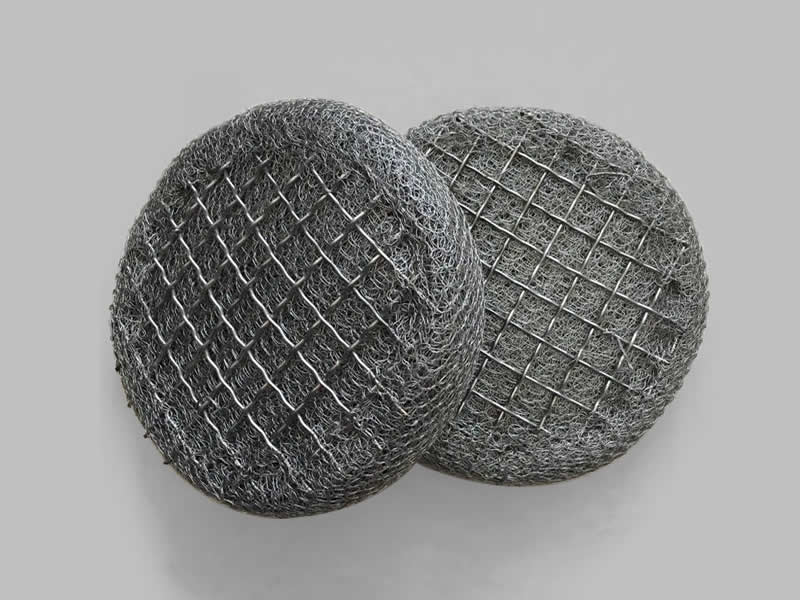

Diameter: Typically 1,000 mm, mid-sized.
Thickness: 150 mm, thicker for greater capacity.
Construction: Main mesh with top and bottom support layers.
Reinforcement: Reinforced top and bottom to prevent warping.
Application: Ideal for high-flow or high-stress systems needing extra support.
Handling: Heavier but more durable under pressure.
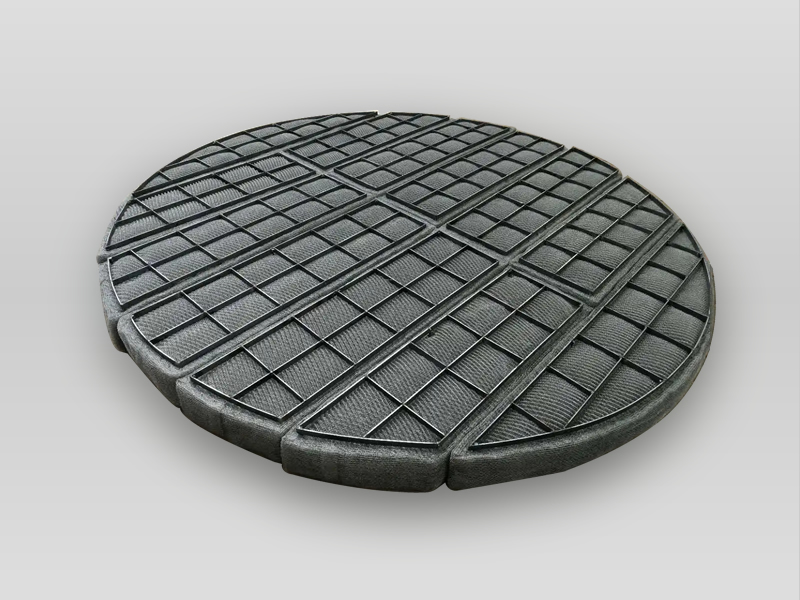

Diameter: 1,000–2,000 mm, offering size flexibility.
Thickness: 100–150 mm, adaptable to various systems.
Construction: Several arc-shaped pieces.
Reinforcement: Mesh distributed across arcs.
Application: Suitable for large tanks where full-size pads are unwieldy.
Handling: Easier transport section by section.
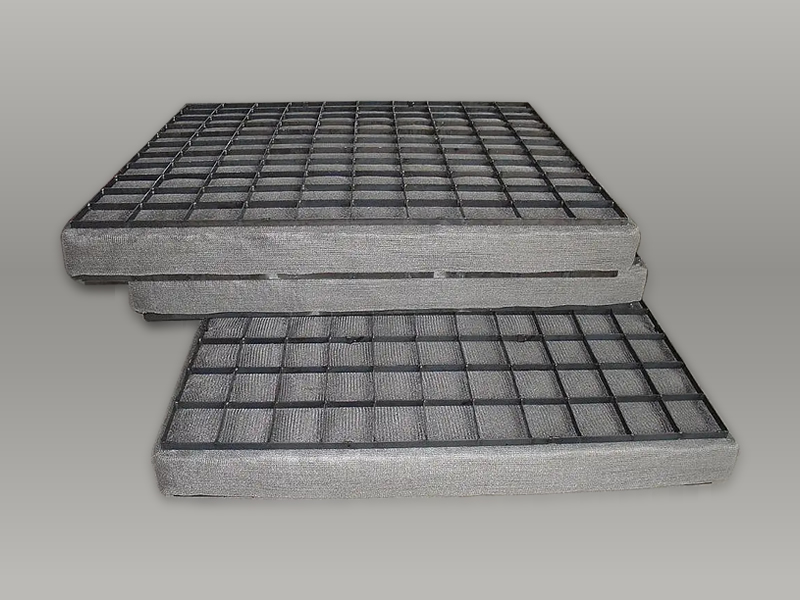

Dimensions: Around 600 mm × 1,200 mm, longer but narrower than some ring.
Thickness: 100–150 mm, similar to reinforced styles.
Construction: Flat rectangular shape.
Reinforcement: Bar grating for internal strength.
Application: Designed for rectangular ducts or chambers.
Handling: Flat shape stacks efficiently.
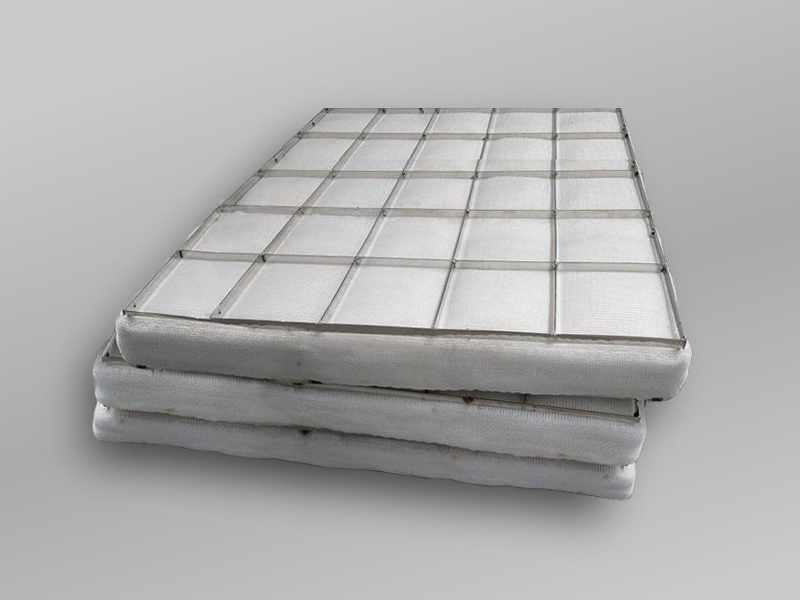

Dimensions: Typically 500 mm × 1,000 mm, smaller than metal versions.
Thickness: Around 100 mm, lighter material.
Construction: Polypropylene with plastic-compatible grating.
Reinforcement: Plastic grating suitable for corrosive settings.
Application: Ideal for chemical or wastewater systems; less suitable for high heat.
Handling: More portable due to lighter weight.